Introduction: The Financial and Emotional Value of Surrogacy
Becoming a surrogate mother is a profound act of generosity, allowing families to experience the joy of parenthood. While many surrogates are driven by a deep desire to help others, the financial compensation involved is also an important consideration. Gaining clarity on surrogate compensation ensures your physical, emotional, and financial needs are met throughout this life-changing journey.
What Does Surrogate Compensation Include?
Surrogate compensation refers to the financial reimbursement provided to a surrogate mother for her commitment to carrying and delivering a baby. This typically includes a base payment along with additional allowances for medical care, travel, and other pregnancy-related expenses. The total compensation package can vary depending on location, experience, and whether the arrangement is through an agency or a private agreement.
For many surrogates, the package is tailored to recognize the significant time, effort, and sacrifices involved. Understanding these details helps ensure fair compensation while maintaining clarity and transparency between the surrogate and intended parents.
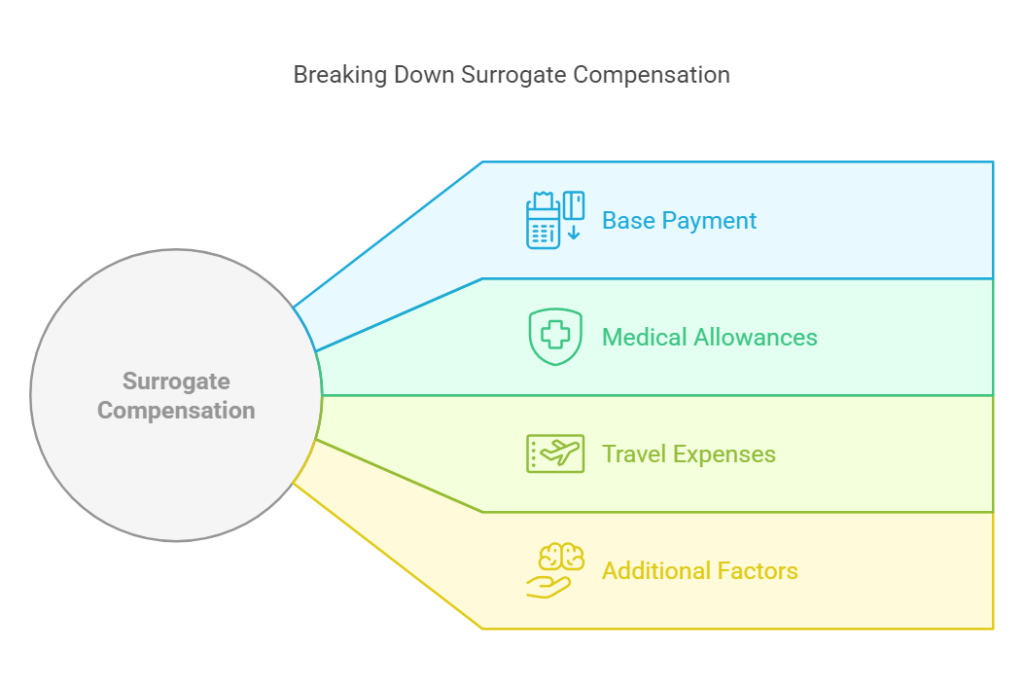
Factors That Impact Surrogate Compensation
Several elements influence how much surrogates receive:
- Location: Compensation tends to be higher in regions where surrogacy services are in high demand, such as California and other surrogate-friendly states in the U.S.
- Experience: First-time surrogates generally receive a standard base fee, while experienced surrogates often negotiate higher rates based on their expertise and proven ability.
Type of Arrangement:
- Agency Agreements: Agencies typically offer standardized packages with clear breakdowns of payments.
- Independent Surrogacy: Private agreements allow for tailored compensation, directly negotiated between the surrogate and intended parents.
Key Components of Compensation Packages
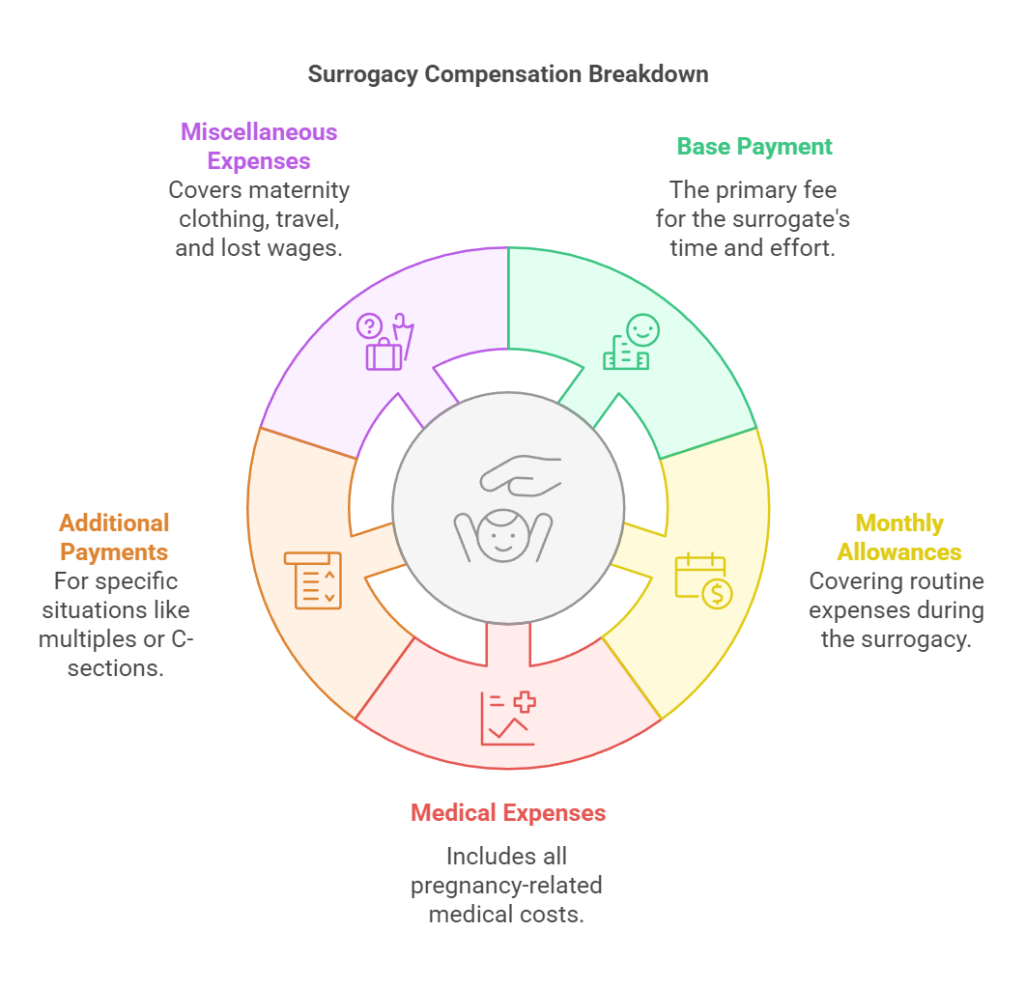
Surrogacy compensation is typically divided into several categories:
- Base Payment: This is the primary fee for the surrogate’s time, effort, and the challenges of pregnancy, often ranging between $30,000 and $60,000 or more.
- Monthly Allowances: Cover routine expenses like transportation to appointments, prenatal vitamins, and childcare.
- Medical Expenses: Includes all pregnancy-related costs, such as IVF treatments, prenatal care, and delivery, usually paid by the intended parents.
- Additional Payments: May cover specific situations like carrying multiples, undergoing a C-section, or meeting other contractual requirements.
- Miscellaneous Expenses: Often includes maternity clothing, travel and lodging for medical visits, and lost wages if the surrogate has to take time off work.
Legal and Tax Considerations
Understanding the legal and tax implications of surrogate compensation is vital:
- Contracts: A legally binding agreement outlines all compensation details, ensuring clarity and protecting the interests of both parties.
- Tax Obligations: In most cases, compensation is considered taxable income. Surrogates should consult with a tax professional to plan appropriately.
The Emotional Rewards Beyond Payment
While financial compensation is a significant aspect, many surrogates emphasize the emotional fulfillment that comes with helping a family grow. The knowledge that you’ve made a life-changing impact can bring immense pride and a sense of purpose. For many, this emotional reward is an invaluable part of the surrogacy experience.
Conclusion: Making an Informed Choice
Surrogacy compensation reflects the tremendous physical, emotional, and time commitments involved in carrying a child for another family. By understanding the components of a compensation package and considering both financial and emotional aspects, you can decide if surrogacy aligns with your personal goals. Whether through an agency or an independent arrangement, having a clear agreement ensures a smooth, rewarding journey for everyone involved.




